Tired of fumbling around with complicated wiring and connections to build electronic devices? Say goodbye to the headache-inducing of connecting multiple PCBs with board-to-board connectors! These innovative components have transformed the world of electronics, making it easier than ever to seamlessly and efficiently connect printed circuit boards.
Discover the incredible power of board-to-board connectors in this must-read article. Get an in-depth understanding of their unique features, types, and applications, plus expert tips for optimizing their performance. Whether you’re an experienced engineer or new to the field, take your BTB connector game to the next level with valuable insights and practical advice. Dive in now!
What is a Board-to-Board Connector?
In electronics and electrical engineering, there’s a powerful tool to help you seamlessly connect two printed circuit boards – the board-to-board connector. These BTB connectors are designed to ensure a secure and reliable connection, with the flexibility to adapt to various design requirements.
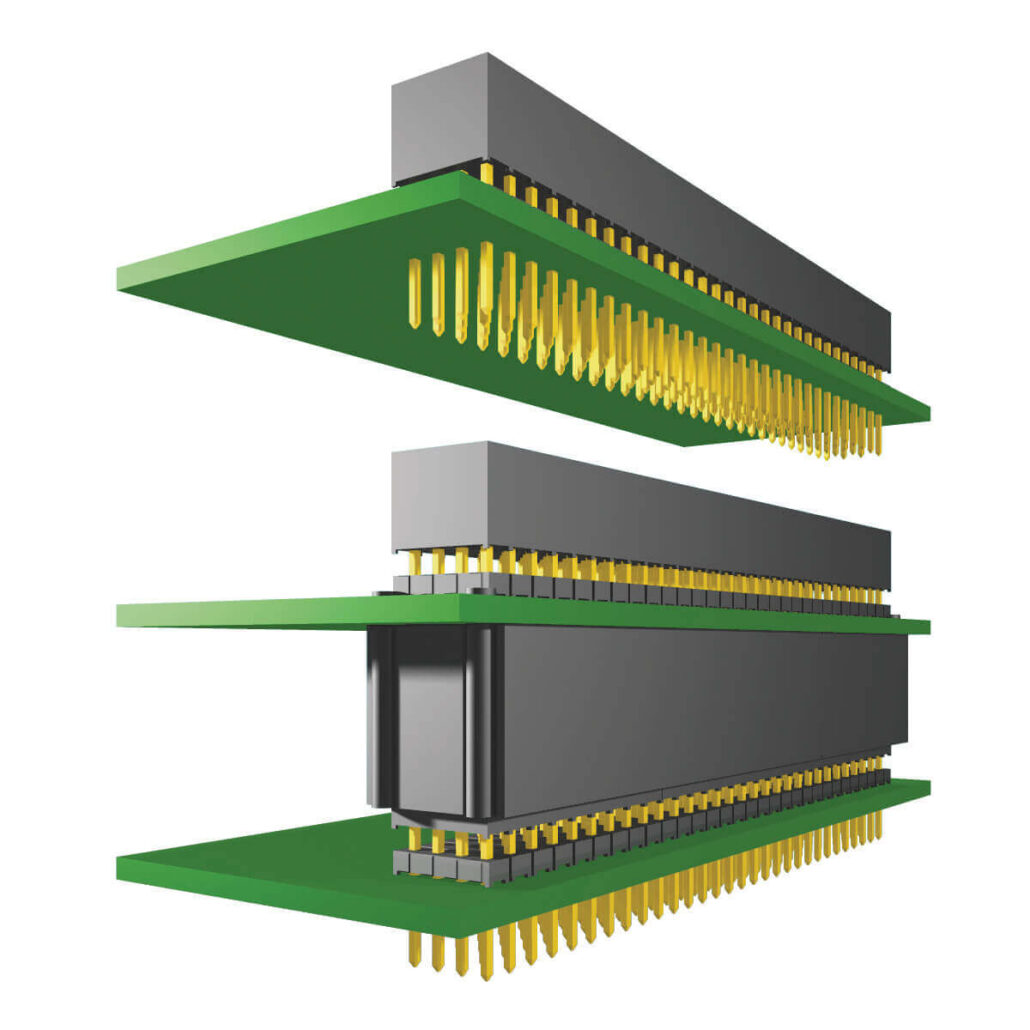
Key Features of Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board connectors are a type of electrical connector that enables the connection of two printed circuit boards (PCBs) or other electronic devices. Here are some of the essential features of board-to-board connectors:
-
Contact Density
Board-to-board connectors offer high contact density, meaning they can accommodate a large number of pins or contacts within a relatively small space. This is particularly crucial in applications with limited space, such as portable devices. In addition, these connectors can have different types of contacts, including surface mount, through-hole, or press-fit.
-
Pitch and Height
The pitch and height of a board-to-board connector are vital to its performance and compatibility with other components. The pitch refers to the spacing between adjacent contacts, while the height is the distance between the PCBs when they are connected. Connectors with reduced pitches and heights are frequently utilized in applications that require limited space.
A low profile is often achieved using a surface mount design, where the connector is soldered directly onto the surface of the PCB.
-
Mounting
Board-to-board connectors can be mounted on the top or bottom of a PCB or between two PCBs. Some connectors are designed for a vertical orientation, while others are intended for a horizontal orientation.
-
Durability
Board-to-board connectors are usually designed to be sturdy and reliable, containing features such as high-temperature materials, locking mechanisms, and polarization. This is essential in applications where the connector may be subject to vibration, shock, or other environmental stresses.
-
Signal Integrity
Board-to-board connectors are often used in high-speed digital and analog applications, so they should be designed to maintain good signal integrity. This can entail incorporating features such as shielding, optimized impedance matching, and minimized insertion loss.
-
Plating and Materials
Board-to-board connectors can be fabricated from different materials, including plastic, metal, and composite materials. The plating on the contacts can also vary, with options including gold, tin, nickel, and silver. The choice of materials and plating can affect the durability, conductivity, and resistance to environmental factors such as corrosion or oxidation.
-
Design Flexibility and Customization
Board-to-board connectors are often designed to be flexible and customizable, with options for different orientations, mounting styles, and contact configurations. Some manufacturers also offer custom design services to create connectors that meet unique requirements.
The features and characteristics of board-to-board connectors may vary based on the specific application and requirements, enabling you to select a suitable connector that meets your needs.
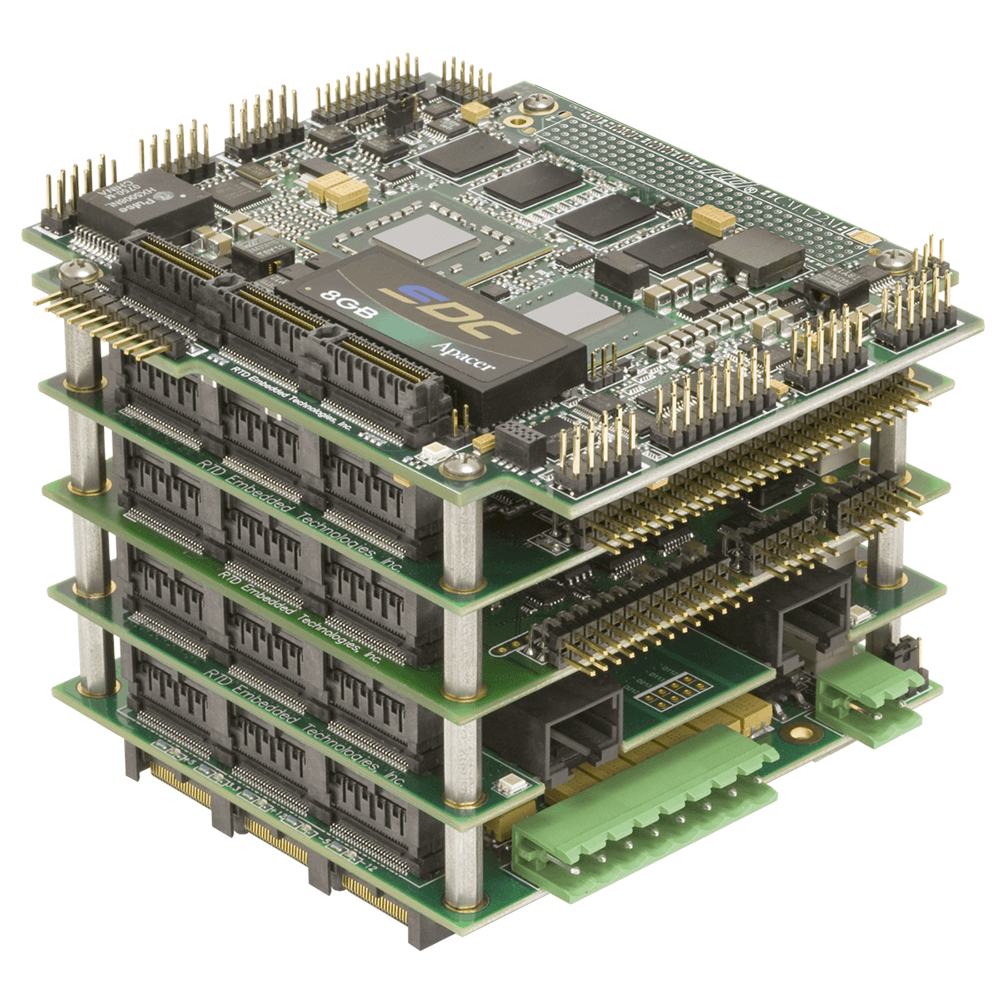
Common Types of Board-to-Board Connectors
Here are just a few examples of the many board-to-board connector types available.
-
Edge Connectors
Designed to be mounted along the edge of a PCB, these connectors have contacts that extend outward and mate with a corresponding connector on another PCB. Edge connectors can be either surface mount or through-hole.
-
Mezzanine Connectors
Mezzanine connectors are commonly utilized in high-density applications where many contacts are needed within a limited space. These connectors may feature multiple rows of contacts and are often designed to be mated at a right angle.
-
FPC Connectors
FPC connectors connect flexible printed circuit (FPC) boards to other PCBs. Typically featuring a low profile, these connectors can be surface mounted.
-
Board Stacking Connectors
Board stacking connectors are engineered to connect multiple PCBs in a vertical stack, with contacts that mate on both the top and bottom of the connector. These connectors can have either surface-mount or through-hole contacts.
-
Memory Card Connectors
These connectors are designed to accept various types of memory cards, including SD cards, Micro SD cards, and others. Memory card connectors typically have a low profile and are surface mounted.
-
High-speed Connectors
These connectors are designed for high-speed data transmission and can be used for applications like USB, HDMI, and other digital interfaces. High-speed connectors often have shielding and other features to maintain signal integrity.

Applications of Board-to-Board Connectors
BTB connectors find their usage in diverse applications across various industries. Here are some examples of how BTB connectors are utilized in different fields:
-
Consumer Electronics
BTB connectors are commonly used in consumer electronics, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and gaming consoles. They are used to connect PCBs to various components, such as displays, cameras, speakers, and sensors. BTB connectors are popular in consumer electronics due to their compact size, high reliability, and ease of assembly.
-
Medical Devices
BTB connectors are widely used in medical devices, where reliable and secure connections are essential for patient safety. They establish the connection between PCBs and a range of components, including sensors, displays, and control units. BTB connectors used in medical devices are often designed to meet strict industry standards, such as ISO 13485, and are required to be highly durable and resistant to harsh environmental conditions.
-
Automotive Industry
BTB connectors are used in the automotive industry to connect PCBs to various components, such as headlights, audio systems, navigation systems, and sensors. They are required to be highly durable, reliable, and resistant to vibration, temperature extremes, and other environmental factors.
BTB connectors used in the automotive industry are often designed to meet industry standards, such as the USCAR-30 standard, and are subjected to rigorous testing to ensure their reliability.
-
Industrial Control Systems
BTB connectors are used in industrial control systems, where reliable and secure connections are essential for the proper machinery and equipment. They connect PCBs to various components, such as sensors, actuators, and controllers. BTB connectors used in industrial control systems are required to be highly durable, resistant to harsh environmental conditions, and able to withstand high levels of vibration and shock.
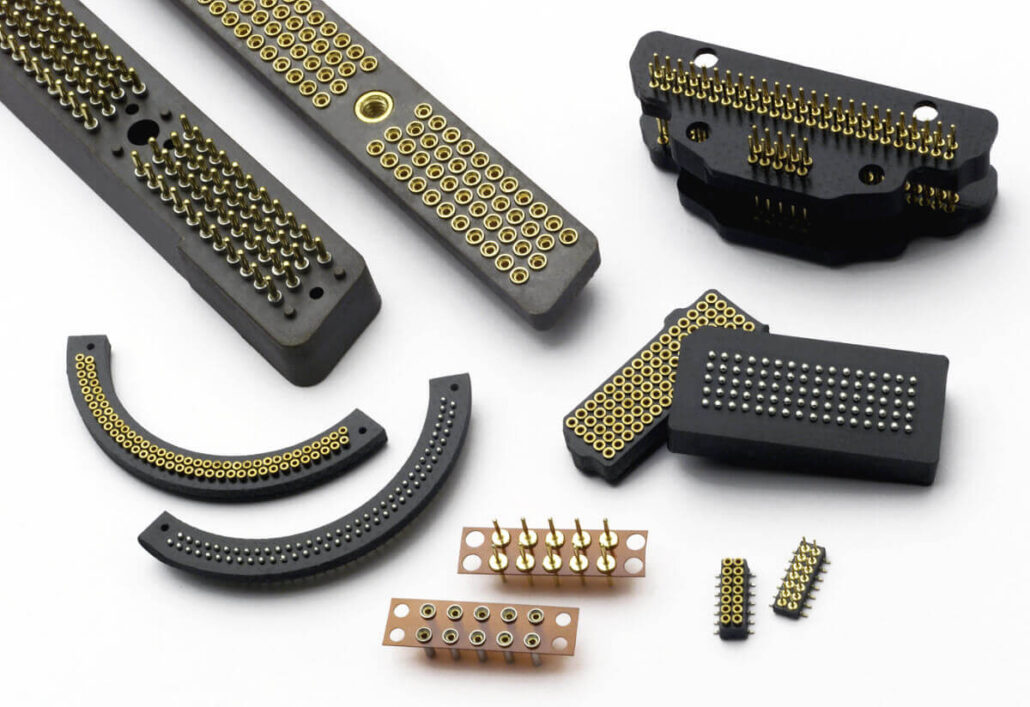

Tips for Optimizing Board-to-Board Connector Performance
Here are some tips for maximizing the performance of board-to-board connectors:
-
Proper Cleaning and Maintenance
Over time, board-to-board connectors may gather dust, debris, and other contaminants that can potentially affect their performance. Clean them regularly using appropriate tools and materials to remove unwanted substances. In addition, keeping the connectors well-maintained can extend their lifespan and reduce the likelihood of issues arising.
-
Using Strain Relief to Prevent Damage
Board-to-board connectors can be subjected to various stresses and strains, especially during installation or when subjected to environmental factors such as temperature changes or vibration. Using strain relief mechanisms, such as clips or cables, can help prevent damage to the connectors and ensure their long-term performance.
-
Ensuring Correct Mating and Alignment
Proper mating and alignment are critical for optimizing the performance of board-to-board connectors. Misalignment or improper mating can lead to poor electrical connections, increased resistance, and reduced performance. Double-checking that the connectors are correctly aligned and mated is a simple but effective way to prevent these issues.
-
Employing Shielding to Minimize Interference
Board-to-board connectors can be susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) that can impact their performance. Employing shielding can minimize this interference and ensure the connectors operate at their best. Shielding can take many forms, including metal enclosures, conductive coatings, or cable shielding.

Future Developments in Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board connectors have been a staple of electronics and electrical engineering for many years, and they continue to evolve and improve with technological advancement. Here are some potential future developments in board-to-board connectors:
-
Higher Data Transfer Rates
With the growing demand for faster data transfer rates in electronic devices, board-to-board connectors may evolve to support higher data rates. This could involve the use of new materials or designs that enable faster signal transmission, such as increased pin density or optimized impedance matching.
-
Smaller Form Factors
As electronic devices become more compact and portable, there is a growing need for smaller board-to-board connectors that can fit in tight spaces. Connectors with smaller form factors, such as micro connectors or wafer-level packaging, may become more prevalent in the future.
-
Enhanced Durability
Electronic devices are often subjected to harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures, vibration, or moisture, which can cause board-to-board connectors to fail. Future developments may focus on improving the durability and resilience of these connectors to better withstand these conditions and extend their lifespan.
-
Advanced Security Features
As the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches continues to increase, the demand for advanced security features in electronic devices is also on the rise. Board-to-board connectors may be designed to incorporate advanced encryption or authentication protocols to ensure data security and prevent unauthorized access.
Across the board, as technology continues to grow, board-to-board connectors are sure to keep up, and new designs and materials will emerge to help meet these evolving needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, board-to-board connectors are an essential component of electronic devices, enabling reliable and efficient communication between printed circuit boards. By understanding the different types of board-to-board connectors, their features, and more, you can optimize the performance of your electronic devices and achieve the best results.
 Over 15 Years of Expertise
Over 15 Years of Expertise FREE samples provided to ensure product satisfaction
FREE samples provided to ensure product satisfaction Rapid Turnaround: Mass Production Complete in 15 - 20 Days
Rapid Turnaround: Mass Production Complete in 15 - 20 Days











