SFP ports are widely used in the field of networking to facilitate high-speed data communication between various devices. These small yet powerful devices play a crucial role in transferring large amounts of data quickly and efficiently. However, understanding the basics of SFP ports, their usage, and the appropriate connectors to use is essential for seamless connectivity and optimal performance.
In this article, we will delve into the world of SFP ports, exploring their functionality, where they can be found, and how they work. We will also discuss the types of connectors that can be used with SFP ports, including both fiber optic and copper cables. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of SFP ports and be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions when it comes to connecting devices using these versatile ports.
What type of connector is used with an SFP port?
People who have to connect devices using fiber optics and copper cables they’re sure to come face-to-face with an SFP port. Regardless of their small size, these devices facilitate the heavy lifting of data communication.
In today’s world of technology, being up to date and having access to your files from the base of your fingertips is a crucial need for all tech wizards. Hence, having a portable yet substantial SFP port that can help transfer an ample amount of data within seconds is vital.
This blog will focus on interpreting an SFP port, how to use it, and most importantly, what type of connector you should use with an SFP port.

What is an SFP port?
An SFP port is a mobile networking device slot that performs the task of transferring data from one device to another. The SFP module is a hot pinky metal component that allows the transmission of information and databases when you connect it using a cable. Regardless of its size and structure, the device can hold large amounts of transmission hosting and is excellent for connecting different connecting devices.
Where can you find the port?
Locating an SFP port is easy because you can easily find it on any networking device such as a router, computer, switch, server, network interface card, etc. Usually, huge computers accommodate two SFP ports so a user can complete the transmission process in minutes. These can sometimes get referred to as SFP switches. Likewise, they’re easily detectable on devices; some even have titles to signify the slot.
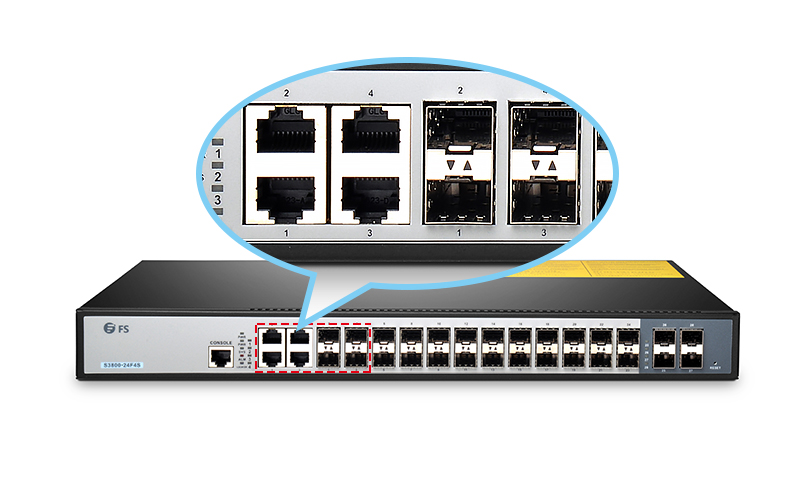

How does an SFP port Work?
An SFP port enables data transmission between two hosts through an SFP transceiver and correct cabling. In simple words, the port and transceiver allow two devices to exchange files by forming a connection through high-quality cables. These can also cater to large distances where portable features come into the picture.
What do you use the device for?
The prime role of an SFP port and its corresponding modules is to develop seamless, high-speed data communication between various networking devices over long distances. At times, they connect one-gigabyte network switch to another; It increases the size and performance ratio of a network, hence increasing functionality.
It turns out to be an excellent favor for the military, industrial, and government settings, where thousands of servers require a high-speed data connection.
Maximum distance an SFP port can accommodate?
The maximum distance supported by an SFP port varies depending on practical considerations, such as the data transfer rate of the SFP module and the type of cables used for the connection. Opting for high-quality cables ensures high-speed connections and determines the distance and performance of the port.

What cable does an SFP port device use?
SFP ports can host fiber optics and copper cable connections. Depending upon the model of an SFP transceiver, the use of copper and fiber optic cable is determined. Small Form Factor Committee only allows for data transfer rates of up to 1 Gbps in an SFP port. Therefore, suppose your network application requires a transmission up to 1 Gbps at 100 meters, then the best option is to opt for a standard Cat 6 ethernet cable.
According to the traditional SFP traditions, a cat six cable easily accommodates the requirements of information conveyance. For faster transfer rates, users can opt for an SFP+ and QSFP+ transceiver with fiber optic cable. These can host an extended distance of more than 100 meters. However, the users will also need the aid of a heavier fiber optic cable.
By using this transceiver, you’ll be increasing your area hold without decreasing or messing with the performance of your SFP port. You’ll also want to purchase a high-category ethernet cable to ensure the process gets carried out seamlessly.

Guide for correctly using a compatible SFP module
The development of fiber optics cables has increased tenfold in recent years thanks to the advancements of the online world. New and improved SFP transceivers are getting manufactured for data centers worldwide to cater to the needs of large networking companies and sites. However, there are still some doubts about the compatibility of an SFP transceiver.
Understanding the concept of multi-source agreement (MSA) is essential if you want to understand SFP compatibility. An MSA is an agreement between transceiver manufacturers so that they can manufacture standardized products. MSA specifies SFP and defines the module’s size, connectors, and signaling to ensure they work ideally with other SFP modules to form a robust connection.
Hence, if you encounter an SFP module with various other cables and ports, while it transmits the data over the region perfectly, users can rest assured that the product is SFP compatible.

How to Use a Compatible SFP Module
Below are some ways you can use a compatible SFP module the right way without disrupting speed, performance, and transmission cables. It’s necessary to understand the proper ways of dealing with these parts, as they hold heavy data from different networks.
- Check your device and transceiver module port.
Many users can easily mix up various transceiver modules for an SFP, including SFP+. Although an SFP can fit in the port easily and perform the task without a hunch, it may cause a hindrance with the transmission limit of 1 Gbps. So, it’s essential to note the right device and port size before you set out to work.
- SFP modules should have identical wavelengths at both ends
The data transmission process includes converting the electrical signals from one side into optical signals and then transmitting the lights through the fiber and converting them into electrical on the other side again. To complete this process without a hunch, the wavelength of either end should be identical. Therefore, looking at SFP module guidelines is crucial.
- Choose the correct fiber type
- Ensure the SFP module is compatible with both ports.
While working with a networking port is crucial to know if it accommodates your SFP module or not. Some brands from vendors may not work compatibly with a port, so checking the standard of a port is highly recommended before starting the process.

Types of SFP Modules
Most SFPs get categorized according to their data compatibilities. Some high data compatibilities range from 100 base, 1000 base gigabytes, and SFP+ or 10 Gigabytes. You can find most SFP ports can offer transmission of 1 gigabyte. However, the advanced version can go up to a 10-25 rate.
Therefore, depending on your work module, picking the correct port for the job is essential. Depending on size, compatibility, and performance, users can find multiple SFP ports in the market. To save you the trouble of juggling with names and models, we’ve compiled a list of all types of SFP modules. SFP transceivers have abbreviations for indicating their size chart like; SX, ZX, LX, EX, etc. These abbreviations indicate the wavelengths of various capacities.
| SFP Module Type | Description | Supported Distance |
|---|---|---|
| 1000BASE-LX 10 | Single-mode fiber, long reach | Up to 10 kilometers |
| 1000BASE-LX | Single-mode fiber | Up to 10 kilometers |
| 1000BASE-SX | Multi-mode fiber | Up to 550 meters |
| 1000BASE-LH | Single-mode fiber, long haul | Up to 70 kilometers |
| 1000BASE-LH/LX | Single-mode fiber, long haul or long reach | Up to 80 kilometers |
| 1000BASE-ZX | Single-mode fiber, extended reach | Up to 80 kilometers |
| 1000BASE-EX | Single-mode fiber, extended reach | Up to 40 kilometers |
Each SFP port can perform for a specific wavelength with a determined distance. For instance, 1000BASE- LX SFPs can conduct a 1310 mn wavelength for a 10-kilometer distance over single-mode fiber. On the other hand, 1000BASE-ZX can cover up to 80 kilometers. Although general SFP ports are available in ethernet switches, NIC cards, firewalls, routers, etc., these ports connect to optical fiber or copper cables. However, Other transceiver types include 3G-12G video SFP, which commonly gets detected in HD cameras.

Benefits of SFP Transceivers
Before we end the blog, let’s quickly look at some SFP Transceiver benefits.
- They are hot-swappable, meaning you can easily take the device out without disrupting the functioning devices.
- Ethernet, SONET, and Fiber Channels are some of the communication standards that SFP works with.
- Another benefit includes Flexibility. SFP can allow design modification, For instance, when starting, the WAN may get disconnected, but after a minute, you won’t need the Fiber optic cable and can take out the port and install it in other devices.
- SFP transceiver modules allow the Ethernet and Fiber optic processes more convenience. Users can take out the SFP without moving the entire board while the device is functioning.
- To monitor the real-time parameters of SFP, users can now use the Digital optical monitoring (DOM) feature set; It helps make daily operations easy and controllable.
- SFP allows more storage space and is more reliable than GBIC. Some technicians even call it an upgraded version of the latter.
- The SFP cage surface rests easily on the top of the PCB board. It helps simplify accepting transceivers. It provides simple and easy reconfiguration and replacements, eliminates manufacturing, and reduces cost.
- SFPs have multiple termination options that allow them the power to communicate over long and short distances.

Conclusion:
SFP ports play a vital role in facilitating high-speed data communication between various networking devices. Understanding the concept of an SFP port, its usage, and the type of connector to be used is crucial for seamless connectivity and optimal performance.
By following the guidelines for using compatible SFP modules and selecting the appropriate cables, users can ensure reliable and efficient data transmission over short or long distances. Whether it’s connecting routers, switches, servers, or other network devices, leveraging the power of SFP ports can enhance the functionality and connectivity of your network infrastructure.
 Over 15 Years of Expertise
Over 15 Years of Expertise FREE samples provided to ensure product satisfaction
FREE samples provided to ensure product satisfaction Rapid Turnaround: Mass Production Complete in 15 - 20 Days
Rapid Turnaround: Mass Production Complete in 15 - 20 Days











